Protecting the health and safety of employees should always be a top priority of any organization, no matter its size or industry. Healthcare facilities routinely use several types of chemicals that are regulated by governmental agencies, including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH), or require documentation for the Joint Commission on Accreditation of Healthcare Organizations (JCAHO). By maintaining a strong occupational exposure monitoring program for these potentially harmful chemicals, employers can ensure proper safety and regulatory compliance.
Scroll down or click the links below to read about some common chemicals of interest used in a healthcare setting. In each section, you can click on the provided exposure limits to find details about the relevant chemical. To learn more about a product or order, click on its Assay Technology product number (e.g. 574AT).
| Halogenated Anesthetic Gases | Nitrous Oxide | Xylenes | Sterilization Chemicals | Formaldehyde |
Don’t see what you’re looking for? You can:
- Review our list of badges.
- Search our dynamic sampling guide.
- Reach out to us by phone or email.
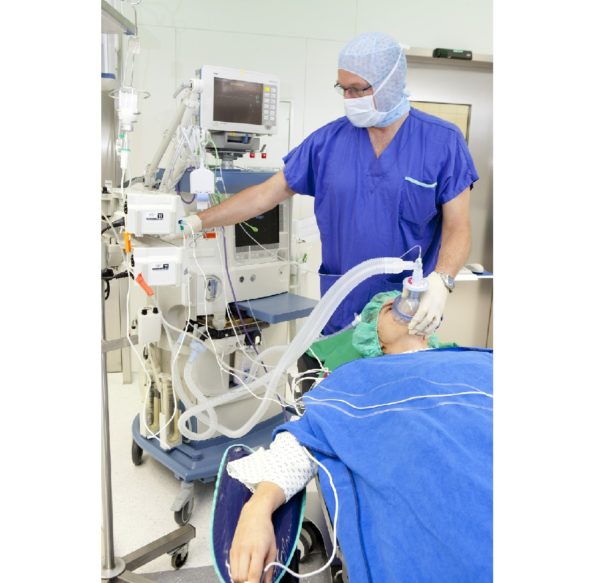
Halogenated Anesthetic Gases
Halogenated Waste Anesthetic Gases, often referred to as HAGs or WAGs, are commonly used during surgical procedures in medical, dental, and veterinary workplaces. These gases include isoflurane (Forane®), sevoflurane (Ultane®), desflurane (Suprane®), enflurane (Ethrane®), and halothane (Fluothane®).
| Exposure Limit | Assay Technology Solution |
| Cal/OSHA PEL: 2 ppm averaged over 8 hours | 574AT |
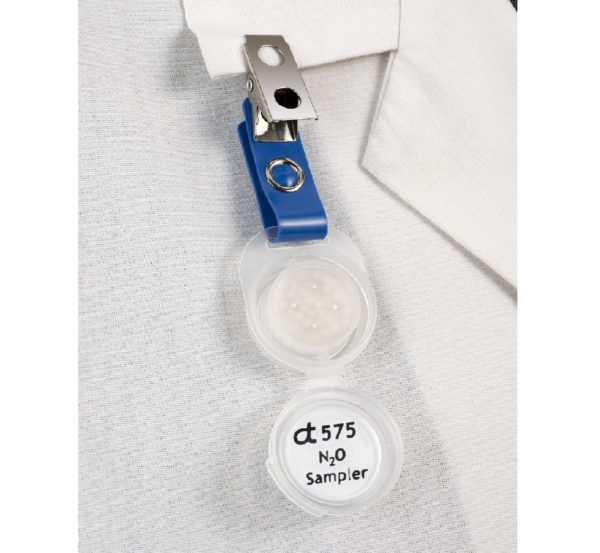
Nitrous Oxide
Nitrous oxide is an anesthetic gas commonly referred to as “laughing gas” or simply “nitrous”. This colorless gas is most often used during procedures in dental clinics, surgical centers, and hospitals.
| Exposure Limit | Assay Technology Solution |
| NIOSH REL: 25 ppm averaged over time exposed | 575AT |

Xylenes
Xylenes are used in pathology and histology labs for specimen preparation.
| Exposure Limit | Assay Technology Solution |
| OSHA PEL: 100 ppm averaged over 8 hours
NIOSH STEL: 150 ppm averaged over 15 minutes |
566AT |

Sterilization Chemicals
A number of different chemicals are used for sterilization of instruments and materials in a healthcare setting. Some of the most common are listed below, along with their regulatory limits and recommended Assay Technology products.
| Chemical | Exposure Limit | Assay Technology Solution |
| Acetic acid | OSHA PEL: 10 ppm
NIOSH STEL: 15 ppm |
543AT |
| Ethylene oxide | OSHA PEL: 1 ppm
OSHA STEL: 5 ppm |
555AT |
| Formaldehyde | OSHA PEL: 0.75 ppm
OSHA STEL: 2 PPM |
571AT |
| Glutaraldehyde | NIOSH CEILING: 0.2 ppm | 581AT |
| Hydrogen peroxide | OSHA PEL: 1 ppm | 587AT |
| OPA (Cidex®) | None set | 581AT |
Formaldehyde in Funeral Homes & Death Services
In addition to its use for sterilization in healthcare facilities, formaldehyde is also a key component used in funeral homes for embalming.
As listed above, OSHA has set exposure limits of 0.75 ppm averaged over an 8-hour period (PEL/TWA) and 2 ppm over a 15-minute period (STEL). Our 571 badge reports results at concentrations as low as 0.01 ppm for 8 hours or 0.34 ppm for 15 minutes.